
OOPS, i.e. Object-Oriented Programming Language is one of the most important concepts which is widely used in the programming world. Every interview that you are attending today requires the knowledge of OOPS. The below article compiles the most frequently asked OOPS Interview Questions and Answers which help you to ace your interviews. If you don’t know object-oriented programming then you can’t think of developing mobile software. Its unique features like inheritance, data hiding which is also known as encapsulation, data binding, polymorphism make it superior to other programming languages.
Popular languages like Java, C++, and Python, etc. are using the concept of the oops model and making it more significant in the programming world. Through OOPs a user can break his program into small-sized problems and that can be solved easily like one object at one time. The system in which the concept of OOP is used can be easily upgraded and hence provides better quality of software, enhances programmer productivity, and lower maintenance cost.
Most Frequently Asked OOPS interview questions
Here in this article, we will be listing frequently asked OOPS interview questions and Answers with the belief that they will be helpful for you to gain higher marks. Also, to let you know that this article has been written under the guidance of industry professionals and covered all the current competencies.
OOPS stands for Object Oriented Programming system. It is a programming technique which is used to design your application. In this programs are considered as a collection of objects and each object is an instance of a class.
You have to list these four features of OOPs while answering this question-
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Encapsulation
- Data Abstraction
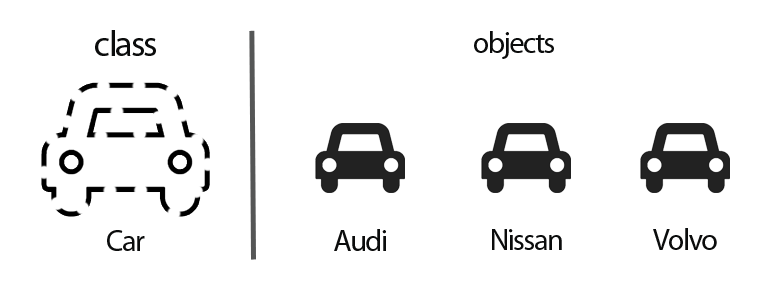
Class
In Object-Oriented Programming, a class is a blueprint that defines the functions and variables which are common to objects of a certain kind.
Object
In OOPS an object is a specimen of the class. It is nothing but a component that consists of methods and properties which make the data useful and help users to determine the behavior of the class.
class Person{
public $name;
function __construct($name){
$this->name = $name;
}
function getUserDetails(){
return "My name is ".$this->name;
}
}
An object is an instance of a class. It has its own behavior and identity.
//Create an object of MyClass
$object = new MyCustomClass();
OR
$object = new MyCustomClass;
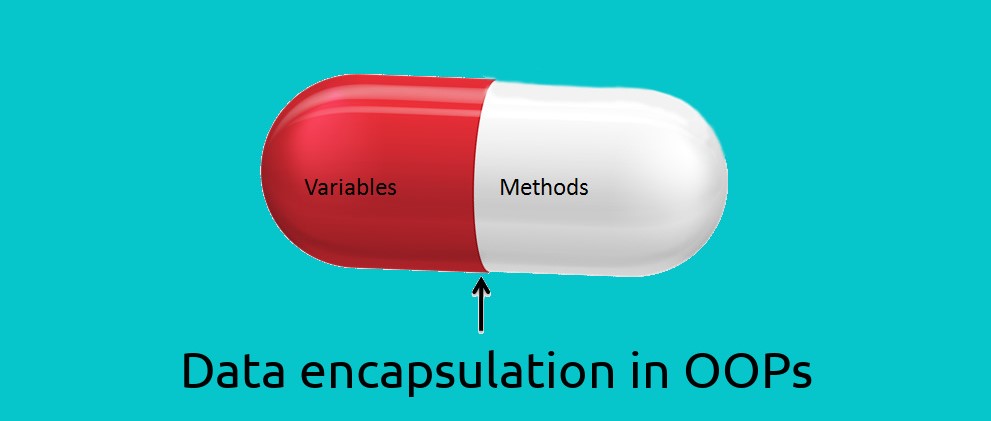
The process of binding up data and functions together that manipulates them is known as encapsulation in OOPS. It protects the data from outside interference and misuse.
Let’s understand the concept of encapsulation with both real-world examples and with the help of a program.
class Account {
private int account_number;
private int account_balance;public void show Data() {
//code to show data
}public void deposit(int a) {
if (a < 0) {
//show error
} else
account_balance = account_balance + a;
}
}
Polymorphism is one of the core concepts which is used in object-oriented programming. Polymorphism generally shows the relationships between parent class objects and child class objects.
Types of polymorphism in OOPs
- Compile Time Polymorphism- It is also known as Static Binding and allows the programmer to implement various methods. Names can be the same but their parameters should be different.
- Runtime Polymorphism- It is also known as Dynamic Binding and allows the programmer to call a single overridden method during the runtime of the program.
It is a technique in which one class acquires the property of another class. With the help of inheritance, we can reuse the fields and methods of the existing class.
Inheritance has three type, are given below.
- Single inheritance
- Multiple inheritance
- Multi level inheritance
But PHP supports only single inheritance, where only one class can be derived from single parent class. We can also use multiple inheritance by using interfaces.
Constructor and Destructor both are special functions which are automatically called when an object is created and destroyed.
Constructor
class Animal
{
public $name = "No-name animal";
public function __construct() {
echo "I'm alive!";
}
}
Destructor
class Animal {
public $name = "No-name animal";
public function __construct($name) {
echo "I'm alive!";
$this->name = $name;
}
public function __destruct() {
echo "I'm dead now :(";
}
}
$animal = new Animal("Bob");
echo "Name of the animal: " . $animal->name;
PHP have three access modifiers such as public, private and protected.
publicscope of this variable or function is available from anywhere, other classes and instances of the object.privatescope of this variable or function is available in its own class only.protectedscope of this variable or function is available in all classes that extend current class including the parent class.
Final Class- A class that can’t be extended and inherited further is known as Final Class. This class is declared with the keyword final and should be declared.
Final Method- Methods in the final class are implicitly final and if a user uses the final keyword that means methods can’t be overridden by subclasses.
class childClassname extends parentClassname {
protected $numPages;public function __construct($author, $pages) {
$this->_author = $author;
$this->numPages = $pages;
}final public function PageCount() {
return $this->numPages;
}
}
Overloading : It occurs when two or more methods in one class have the same method name but different parameters.
Overriding : It means having two methods with the same method name and parameters. One of the methods is in the parent class and the other is in the child class.
It refers to the current object of a class.
Thera are many differences between abstract class and interface in php.
1. Abstract methods can declare with public, private and protected. But in case of Interface methods declared with public.
2. Abstract classes can have constants, members, method stubs and defined methods, but interfaces can only have constants and methods stubs.
3. Abstract classes doest not support multiple inheritance but interface support this.
4. Abstract classes can contain constructors but interface doest not support constructors.
It allows us to use the same function or class name in different parts of the same program without causing a name collision.
namespace MyAPP;
function output() {
echo 'IOS!';
}
namespace MyNeWAPP;
function output(){
echo 'RSS!';
}
Traits is a group of methods that reuse in single inheritance. A Trait is intended to reduce some limitations of single inheritance by enabling a developer to reuse sets of methods.
trait HelloWorld
{
use Hello, World;
}
class MyWorld {
use HelloWorld;
}
$world = new MyWorld();
echo $world->sayHello() . " " . $world->sayWorld(); //Hello World
Magic methods are special names, starts with two underscores, which denote methods which will be triggered in response to particular PHP events.
The magic methods available in PHP are given below:-
- __construct()
- __destruct()
- __call()
- __get()
- __set()
- __isset()
- __unset()
- __sleep()
- __clone()
- __autoload() etc
- Code Resusability
- Flexibility
- Maintainability
- Security
- Testability
Member variables defined inside a class. Data of member variables will be invisible to the outside of the class and can be accessed via member functions. These variables are called attribute of the object once an object is created.
Member function defined inside a class and are used to access object data.
We have three different types of Class Variables in OOPs.
1. Local Variables
These types of variables are declared locally in methods, blocks, and constructors. These variables are created when program control enters the methods, blocks, and constructor and are destroyed once program control leaves them.
2. Instance Variables
These variables are declared outside a block, constructor, or method. These are created once a class object is created and destroyed when the object is destroyed.
3. Static Variables
Static variables are also called class variables and are defined using the static keyword. These are declared within a class but outside a code block and a method. The creation of these variables starts when the program starts and is destroyed when the program ends.
There are certain points due to which OOPs become so popular.
- It provides a better programming style, so you don’t need to write code again and again which you want to run, just make a class of the object and call it.
- As it supports the inheritance concept, an application created with OOPs can inherit another class property.
- It provides a modularity model that means if you change any part of code that is in a separate module, that won’t impact any other module.
- If you are stuck somewhere, this language allows your problems to break down into bite-sized pieces so that you can solve them.
- Due to its polymorphism feature, a single class can be used to create different objects, and that too from the same piece of code.
| Method Overloading | Method Overriding |
|---|---|
| It is the concept where we define two or more methods by the same name but with different signatures. | In method overriding we define two or more identical methods which have the same name and signatures. |
| The binding of the method is done at compile time. | The binding of the method is done at run time. |
| There are no class restrictions i.e. it can be achieved in the same or different classes. | There are class restrictions in it i.e. it can only be achieved in different classes. |
| Virtual Function | Pure Virtual Function |
|---|---|
| Virtual Function has its definition hidden in the Base class | They have no definition in the Base class. |
| The derived class can override the virtual function if required. | In the case of a pure virtual function, the derived class has to override it. |
| If the derived class fails to override then it has the option to use the virtual function of the base class | It will throw a compilation error if it fails to override pure virtual function. |
| CLASS | OBJECT |
|---|---|
| It is a blueprint from which different instances (objects) are created. | Objects are the instances of the class. |
| Class is a logical entity. | Objects are physical entities. |
| Users can declare class only once. | Objects can be declared multiple times depending upon the requirements. |
| When a class is created there is no memory allocation | Objects allocated memory. |
| Class is a group of objects. | Objects are real-world entities such as pen, copy, mouse, etc. |
| Class can be declared using class keyword e.g class Student {} | Objects can be declared using the new keyword e.g. Student s1=new Student(); |