
In this world full of development firms we all know how useful Server Side Scripting is. Node.JS is also server-side scripting with the help of which you can build anything, starting from a single program to a complex web application. And that’s why Certified Node.JS developers are in too high demand. Node.JS opens many opportunities for you and to grab you those opportunities we have compiled a popular list of Node.JS Interview Questions and Answers. These questions will also help you to clear all your basic concepts of Node.JS.
It is a web application framework that is built on Google Chrome Javascript’s Engine that compiles JavaScript into machine code and reduces development costs by 58%. This backend framework has been worldwide accepted and can be used in real-time web applications, network applications, single-page applications, etc. In the year 2018, this framework hits 1 billion downloads and you will be surprised to know that Node js powers over 30 million sites out of which 6.3 million sites are from the U.S alone. Developers who are looking for a change and want to give their career a boost, we assure you this list of interview questions surely uplift your confidence.
What's in it for me?
We have created this section for your convenience from where you can navigate to all the sections of the article. All you need to just click on the desired section, and it will land you there.
Most Frequently Asked Node js Interview Questions
Here in this article, we will be listing frequently asked Node js Interview Questions and Answers with the belief that they will be helpful for you to gain higher marks. Also, to let you know that this article has been written under the guidance of industry professionals and covered all the current competencies.
Node.js, as open-source server environment, runs on various platforms such as Windows, Unix, Linux, etc. The anchor of the MEAN stack, Node.js is also one of the most popular server platforms in the world.
Why it is used?
- It is asynchronously programming, runs single-threaded, non-blocking which is very memory efficient.
- It can operate file various operations like create, open, write, read, delete, and close files on the server and can collect form data.
- Scalable and extensible
- Easy to learn
- Used as a Single Programming Language
- Offers benefits of Fullstack JS
- Offers High Performance
The NPM provides two main functionalities:
- It is the online repository for all of the Node.js packages.
- It is the command line utility for installing, version management and dependency management of the Node.js packages.
- Go to the Nodejs.org site and download the binary files and Windows installer.
- Run the Windows installer.
- Follow the instructions on the screen for accepting the license agreement, clicking the NEXT button a few times and allowing the default settings.
- You will have to restart your computer. Remember that you may not be able to run Node.js until you restart your computer.
- Make sure you have installed Node by running simple commands just to see what version got installed.
A callback function is done at the completion of a task. This function allows other codes to be run in the meanwhile and prevent blocking. Because Node.js is an asynchronous platform, it relies heavily on the callback function. In addition, the APIs also support callbacks.
package.json is the most important file of any Node.js project and it contains the metadata of the project. It is used to give information to NPM that allows it to identify the project. It handles the project's all dependencies. It is placed on root of any project.
We can avoid callback hell by different available solutions, as mentioned below.
Promises: The promise is s result of an asynchronous operation. We can create a promise on these three states:
- Pending: When the initial state is not fulfilled or rejected.
- Fulfilled: When the operation gets completed successfully.
- Rejected: When the operation gets failed.
Generators: These are functions that can be resumed and paused. It doesn’t get executed immediately when called. Instead, it returns a generator object or generator object with which we can control the execution of the function.
Note: After learning the basics of Node, if you are looking for what more to learn, you can start with meta-programming, protocols, and much more. We have created a list of node interview questions to help them use this language to solve complex problems.
The Read Eval Print Loop (REPL) performs these four tasks - Read, Evaluate, Print and Loop. The REPL is used to execute ad-hoc Javascript functions. The REPL shell allows direct entry of javascript into a shell prompt and evaluates the results. REPL is very critical for testing, debugging, or experimenting.
Node.js and Asynchronous JavaScript and XML (Ajax) are the advanced implementations of JavaScript. Ajax is designed for dynamically updating a section of a page’s content, without having to update the entire web page. Node.js is utilized for developing client-server applications.
Both Node.js and jQuery are the advanced implementations of JavaScript. Node.js is a server-side platform for developing client-server applications. However, Node.js can also run on a server similar to Apache and Django, but not in a browser. jQuery is a JavaScript module that complements AJAX, looping, DOM traversal. It provides useful functions that help in JavaScript development. jQuery also manages cross-browser compatibility and can help produce extensive web applications.
Point to be noted: Go through this Q&A very thoroughly as this is one of the critical node js interview questions.
This is a mechanism by which the output of one stream is connected to the output of another stream y creating a long chain of multiple stream operations.
Streams are the objects that allow and enable the continuous process of reading the data from the source code and writing the data to the destination.
Streams are of four types:
- Facilitate reading operation (Readable).
- Facilitate writing operation (Writable).
- Facilitate both reading and writing operations (Duplex).
- Kind of duplex stream that performs the computations based on the available inputs (Transform).
Exit codes are the specific codes that can be used to end a process. Some of the examples of exit codes are, Uncaught Fatal Exception, Fatal Error, Non-function Internal Exception Handler, Internal Exception handler Run-Time Failure, Internal JavaScript Evaluation Failure, etc.
Node JS is used to develop server side applications but Angular JS is used to client side applications.
Node JS was developed by Ryan Dahl in 2009 but Angular JS developed by Misko hevery( Google developer ) in 2008 and 2009.
Both are open-source tools that is used to create isomorphic web applications
It is a returned value by an asynchronous function to indicate the completion of the processing carried out by the function.
var promise = doSomethingAync()
promise.then(onFulfilled, onRejected)
It is the process of creating fake endpoints in code so that we can delay writing complex code.
- It is compatible with Node js
- It comes with predefined or usable extensions
- It is simple,lightweight
we have to set flags on the set-cookie HTTP header:
- HttpOnly
- secure
After this it will lokk like this : Set-Cookie: sid=
Point to be noted: Make sure that you go through this twice as this is the favorite node js interview questions for fresher and experienced as well.
It is used to include modules from external files. It takes one string parameters( location of file ) that we want to include.
require('file location')
It was created especially as an examination in async processing. The hypothesis was that performing async processing on to a single thread could give more execution and adaptability under average web loads than the common thread-based usage.
$ sudo npm install npm -g
/usr/bin/npm -> /usr/lib/node_modules/npm/bin/npm-cli.js
[email protected] /usr/lib/node_modules/npm
Buffer
It is a global class that can be accessed in an application without importing the buffer module. It can be constructed in a variety of ways like var buf = new Buffer(5);
Use of a buffer in Node JS
Buffer is used to dealing with TCP streams, reading, and writing data to the filesystem in the Node.js server, which are purely binary teams of data.
It is designed in a way that is easy to manage, faster and has an API designed for binary data, which makes it the perfect choice for handling streams of data.
Stream
these are the objects that allow the developers to read the data from the source or can write the data to the destination in an endless manner. They usually have problems with the large data. With a stream, there is no need to wait for the whole resource to load.
There are different types of Stream:
- Readable
- Writable
- Duplex
- Transfer
A pipe is a function that reads the data from a readable stream once it is available and writes it in the destination writable stream. It performs all the reasonable things including the errors, files in case any one side falls apart. In due case, piping redirections any readable stream to a writable stream.
- newListener
- removeListener
- EventEmitter: 'removeListener'
- EventEmitter. listenerCount (emitter, eventName)
- EventEmitter.defaultMaxListeners
- emitter.addListener(eventName,listener)
- emitter.emit(eventName[,...args])
open() function is used to opens a file by passing a file name.
Syntax : fs.open(path, flags[mode], callback)
Parameters
- path : It is a string having file name with complete path
- flags : It indicates the behavior of the file to be opened
- mode : It sets the file mode like permission
- callback : gets two arguments (err, fd)
var fs = require("fs");
// Asynchronous - Open a File
console.log("open file");
fs.open('file.txt', 'r+', function(err, fd) {
if (err) {
return console.error(err);
}
console.log("File opened");
});
Syntax of read a file is given below:-
fs.read(fd, buffer, offset, length, position, callback)
var fs = require("fs");
var buf = new Buffer(1024);console.log("open existing file");
fs.open('file.txt', 'r+', function(err, fd) {
if (err) {
return console.error(err);
}
console.log("File opened");
console.log("read the file");
fs.read(fd, buf, 0, buf.length, 0, function(err, bytes){
if (err){
console.log(err);
}
console.log(bytes + " bytes read");if(bytes > 0){
console.log(buf.slice(0, bytes).toString());
}
});
});
Syntax of write a file is given below :-
fs.writeFile(filename, data[, options], callback)
var fs = require("fs");
console.log("Write in existing file");
fs.writeFile('file.txt', 'This is test msg', function(err) {
if (err) {
return console.error(err);
}
console.log("Written successfully!");
console.log("Read latest written data");
fs.readFile('file.txt', function (err, data) {
if (err) {
return console.error(err);
}
console.log("Read: " + data.toString());
});
});
Syntax of close a file is given below :-
fs.close(fd, callback)Syntax of delete a file is given below :-
fs.unlink(path, callback)setTimeout() : It can be used to schedule code execution after a designated amount of milliseconds.
function myFunc(arg) {
console.log(`arg was => ${arg}`);
}
setTimeout(myFunc, 1500, 'funky');
clearTimeout() : It can be used to cancel timeout which are set by setTimeout().
console.log('before immediate');
setImmediate((arg) => {
console.log(`executing immediate: ${arg}`);
}, 'so immediate');
console.log('after immediate');
There are two types of API in Node JS.
- Blocking functions
- Non-blocking functions
A test pyramid is a metaphor that helps the grouping of software tests in a bunch of different granularity. Unit testing pyramid number of tests gets easily fitted.
For instance, unit testing, component testing, integration testing, system testing, end-to-end testing, UI testing, and others. The primary example of it is creating a unit test which will be the fastest and reliable.
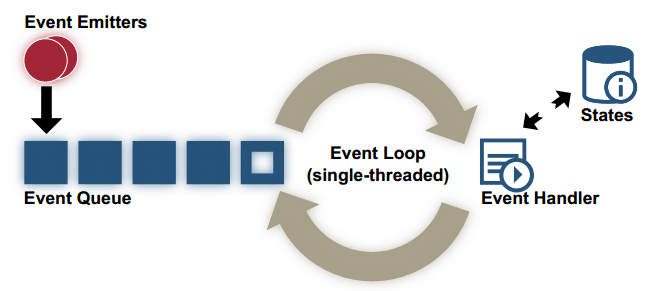
The timing feature of node.js contains all the necessary functions that are required to execute code after any specific period. As it is built on the V8 JavaScript engine of Google Chrome, hence its library permits the fast execution of code. Timers also provide a number of ways for managing schedules. They don't need to be imported as all the methods are easily available for the browser.
Some modules are –
setTimeoutsetIntervalsetImmediateclearImmediate(immediate)clearTimeout(timeout)
Express app encapsulates your API logical, which is your data abstraction. This is where you should keep up your DB logic or data models.
The server should be differently handled as its sole responsibility is to keep the app/website running. The separation of concerns will lead to optimization.
setImmediate() executes a script once the current poll or the event loop phase has completed.
setTimeout() is used to schedule scripts to be run after a minimum threshold has elapsed.
The order in which these timers are executed varies on the context in which they are used. If both are called from within the module, timing will be bound by the process performance.
Node.js appeared when the engineers of JavaScript expanded it from something you could just keep running in the browser to something you could keep running on your machine as an independent application. The Node run-time environment incorporates all that you have to execute a program written in JavaScript.
Some tools and IDEs are -
- Mocha.js
- Chai
- Sinon.js
- Express.js
- WebStorm IDE
- Passport.js
- Cloud9
- IntelliJ IDEA
- Sublime text
Error-first callbacks are generally used to pass errors as well as data. It is important to pass the error as the first parameter, and then you must check if something went wrong. There are additional arguments that are used to pass data.
| Operational errors | programmer errors |
|---|---|
| They are not a bug | They are the actual bug |
| They are not a bug | They are the actual bug |
| They can't corrupt | can corrupt the whole system |
| It refers to know cases | It refers to unknown cases |
| Example: you can consider request timeout for any hardware failure | |
Hapi.js or Express.js is robust and modular for developing the APIs. It has input validation, configuration functioning, and many other features.
Express js is a type of framework which is used for node js. It released under the MIT License. It helps to manage a server and routes. It is also designed for building web applications and APIs.
It was founded by TJ Holowaychuk. The first release of express js was on the 22nd of May, 2010. Version 0.12.0.
Features of Express framework:
- It can be used to design single-page or multi-page web applications.
- It helps to setup middlewares to respond to HTTP Requests.
- It helps us to render HTML Pages dynamically.
Command “require” is used in Node JS for import external libraries. Mentioned below is an example of this. “var http=require (“http”)”. This will load the library and the single exported object through the HTTP variable.
- Node.js lacks consistency, and its API changes frequently.
- It requires more time for development, which affects productivity.
- Users who prefer heavy computing applications cannot find it reliable
- It is advanced, but there are a few poor qualities of tools present in it.
Yes, system configuration need to install nodejs that's are given below-
- 64-bit architecture
- Kernel version 3.10 or higher
-
One of the following Linux flavors
- Ubuntu 14.04 / 15.10
- CentOS 6.x
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 7.x
- Debian 7.7
-
4 or more CPUs/cores
- At least 16 GB of memory/RAM
- At least 25 GB of disk space
-
Ports opened for inbound TCP traffic:
- 8800 (admin console)
- 8080 (registry)
- 8081 (website)
-
Access to the public internet, either directly or via proxy
Consistent style can help your team members modify projects easily without the need to learn a new style for every project. Some of the useful tools are Standard and ESLint.
Reactor Pattern is used for non-blocking Input/Output operations in the Node.js. This pattern provides a handler that is associated with I/O operations. When I/O requests are generated, they get submitted to a demultiplexer, which handles concurrency in non-blocking I/O mode and collects requests in the form of an event and queues the events.
Note: This Node js interview questions have been created by Node.js Experts. It shall help you to answer some of the most frequently asked questions during a job interview.
The Long Term Support (LTS) version of Node.js receives all of the critical bug fixes, performance improvements, and security updates. The LTS versions are supported for at least 18 months and are always even version numbers. They are best for production because the LTS release line focuses on stability and security.
They have globally installed packages or dependencies that are stored in the
Local mode is the package installation in the node-modules directory in the same folder where Node application is stored. By default, the Node Package Manager (NPM) installs dependencies in the local mode. Most locally deployed packages are also accessible via require(). In order to install a Node project locally, you need to follow the syntax.
You can try the following command for uninstalling the module.
C:\Nodejs_WorkSpace>npm uninstall dependency-name
EventEmitter class lies in the events module and is accessibly through the following syntax:
//import events module
var events = require('events');
//create an eventEmitter object
var eventEmitter = new events.EventEmitter();
In case an EventEmitter instance is facing error, it emits 'error' event. When a new listener is added, the 'newListener' event gets fired and when a listener gets removed, 'removeListener' event gets fired.
Every method in the fs module contains synchronous as well as asynchronous form. Asynchronous methods take the last parameter as completion function callback and the first parameter as an error. It is advisable to use asynchronous methods instead of synchronous methods because asynchronous would never block the program execution, but synchronous may block.
V8 Engine is Google's open-source javascript and written in C++. It is used inside Google Chrome. It was first designed to increase the performance of JavaScript execution inside web browsers.
The array of records can easily be bulk inserted into the node.js. Before insertion, you have to convert it into an array of arrays.
var mysql = require('node-mysql');
var conn = mysql.createConnection({
// your database connection
});
var sql = "INSERT INTO Test (name, email) VALUES ?";
var values = [
['best interview question', '[email protected]'],
['Admin', '[email protected]'],
];
conn.query(sql, [values], function(err) {
if (err) throw err;
conn.end();
});
- Step1. Install Async first with "npm install async" command
- Step2. Call the async in your file with you will use async.
var async = require("async"); - Step3. Make an async function and call await function inside async function.
let phoneChecker = async function (req, res) {
const result = await phoneExistOrNot();
}
exports.phoneChecker = phoneChecker;
await will work only under async function.
For example: here is " phoneChecker " is async function, and phoneExistOrNot is await service. - Step4. Now you can write your logic in await function.
let phoneExistOrNot = async function (req, res){
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
db.query('select name, phone from users where phone = 123456789 ', function (error, result) {
if(error) {
reject(error);
console.log('Error');
} else {
resolve(result);
console.log('Success');
}
})
});
}
You can use req.connection.remoteAddress to a user's IP address in node js.
| S.no | let | const |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | It can be reassigned, but can’t be redeclared in the same scope. | It can be assigned an initial value, but can’t be redeclared in the same scope, and can’t be reassigned. |
| 2. | It is beneficial to have for the vast majority of the code. It can significantly enhance your code readability and decrease the chance of a programming error. | It is a good practice for both maintainability, readability and avoids using magic literals |
If you don't install MySQL then you can install MySQL by npm install mysql.
Create Connection
You can write connection code in a single file and call in all pages where you need to interact with database.
var mysql = require('mysql');
var con = mysql.createConnection({
host: "localhost",
user: "your database username",
password: "database password"
});
con.connect(function(err) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Database Connected!");
});
The request object in Node JS represents an HTTP request plus it has properties such as req.app, req.baseURL, etc. to serve the request query parameters, string, body, and HTTP headers, etc.
Nodemon is that tool which helps to develop application based on node.js by automatically re-initiating the application of node whenever the file changes inside the directory get detected.
It does not need any further changes to the code or the development method. Nodemon is the replacement wrapper of Node, to practice Nodemon replace the node word on the line of command at the time of executing the script
In Node.JS, module.exports is a special object that is included in every JavaScript file present in the Node.JS file default. Here module is a variable that represents the current module, and export is the object that will be exposed as the module.
Here we export a string from testYourModule.js file
// testYourModule.js
module.exports = "Best Interview Questions provides an example of module.exports"
// index.js
const params = require('./testYourModule.js')
console.log(params )
When one function simply allows another function being the argument, this enclosed function is called the callback function. And using this callback function is one core concept of functional programming, and the user can also find them inside the most of the JavaScript codes- either inside the simple functions such as setInterval, or event listening or at the time of making the API calls.
The promise, on the other hand, is practiced to manage the asynchronous outcome of one operation. JavaScript has been designed such that it can not wait so that the asynchronous code block can execute completely before the other synchronous code parts can run. With the help of Promises, the users are able to delay the code block execution until the async request gets completed. In this manner, all other operations get to keep running that too without any interruption.
Promise.all([p1, p2]).then(values => {
console.log(values); // [7, "123"]
});
ExpressJS is one prebuilt framework of NodeJS that can assist the users in building server-side web apps faster plus smarter. Simplicity, flexibility, minimalism, scalability are a few of its many characteristics and as it is built inside NodeJS itself, Express inherited its execution as well.
ExpressJS streamlined coding in Node JS to a great extent and provided programmers some extra features to increase their coding of the server-side. There is no doubt in the fact that it is the most famous frameworks of all in today’s time.
Representational State Transfer or REST is a standard web-based architecture. REST makes use of the HTTP Protocol. It twirls around resources where each and every element is one resource and the resource is obtained by the common interface with the help of standard HTTP methods. This was first proposed by a man named Roy Fielding in the year 2000. The REST Server solely renders entrance to resources as well as REST client accesses plus modifies these resources with the help of the HTTP protocol. And here each and every resource is recognized by URIs or by global IDs. It uses numerous representations to present the resource such as text, or JSON, or XML, etc.
With the help of Promises, Handling error across numerous asynchronous calls has become more effortless in comparison to what it was at the time of using callbacks. Also, having the privilege to not provide any callbacks makes the coding look even cleaner. On the contrary, callbacks present the mechanism of control flow. And they only inform the users about how the application flows, and not really the information of what it does.
The paper “The Protection of Information in Computer Systems” by Jerome Saltzer and Michael Schroeder, cited some 8 principles with the help of which information within the computer systems can be stored efficiently. These are mentioned below :
- Least Privilege
- Fail-Safe Defaults
- Mechanism Economy
- Complete Meditation
- Open Design
- Privilege Separation
- Least used Mechanism
- Psychological Acceptability
It extracts the complete body portion owned by the stream of the incoming requests and exposes this extraction on the “req.body like something that is easier to interact with. This renders the user the middleware that uses the nodeJS or the zlib for unzipping the incoming data of request if it is zipped plus stream-utils or the raw-body in order to anticipate the full and raw contents belonging to the body of the request before "parsing it".
The point of differences mentioned below will help you to understand which one is more secure and when:
- If standardization and security are the main goals, then SOAP should be considered as the stronger one to practice as the Web Services. Also, SOAP offers WS-Security which is like an extra perk to the enterprise.
- The REST API is compatible with a number of types of data outputs including JSON, XML, CSV while SOAP is able to handle XML only. With the help of REST using JSON helps to cut down a lot on the expenses.
- REST is further advanced, therefore when the next endpoint requests one query completed beforehand, the development of API can make use of the data that too from the earlier request. Whereas, SOAP implementations need to process all the queries each and every single time.
Although it sounds as if SOAP is more advantageous than REST, yet one good REST implementation can be really beneficial for an enterprise rather than using the poorly-designed SOAP API. And SOAP possesses in-built error handing to communicate errors through the specification of WS-ReliableMessaging. Whereas, REST needs to send the transfer again every time it encounters one error.
JSON Web Token is shortly verbose, this makes JSON compact in terms of size. And JWT becomes the better choice in order to be practiced in HTML plus HTTP environments. And the usage of JWT on the Internet-scale rises the efficiency concerning client-side processing of the tokens on numerous platforms simultaneously.
Callback hell is a situation in Javascript when you face callbacks within callbacks or nested callbacks.
It looks somewhat like this:
firstFunction(args, function() {
secondFunction(args, function() {
thirdFunction(args, function() {
});
});
});
There are two significant ways to avoid Callback Hell in NodeJS:
1. Using Promises
const makeBurger = () => {
return getChicken()
.then(chicken => cookChicken(chicken))
};
makeBurger().then(burger => serve(burger));
See, it is just more easy to read and manage in comparison to the nested callbacks.
2. Use Async/Await
Using Asynchronous functions, we can convert makeBurger into one synchronous code. Also, maybe you can get helpers to getBun and getChicken at the same time, meaning, you can use await with Promise.all. Here's the code:
const makeBurger = async () => {
const cookedChicken = await cookChicken(chicken);
return cookedChicken;
};
makeBurger().then(serve);
| Pure Pipes | Impure Pipes |
|---|---|
| This will thoroughly read the file into the memory before making it available to the user. | It will read chunks of a file as per specifications provided by the user. |
| Since the whole data is sent after it has been loaded, it will take time for the client to reach and hence, is slower. | Since it reads files in chunks, the client will read the data faster than in readFile. |
| It is easier to clean the non-used memory by Node.js in this. | It is much more difficult for Node.js to clean up memory in this case. |
| It will not scale the requests at a given time, preferably all at once. | It will pipe the content directly to the client using HTTP response objects, making it time-saving. |
Note: Our aim while creating nodejs interview questions, is to help you grow as a Node Developer. The questions mentioned here have been asked by leading organizations during technical rounds of the interview process.
Here are some of the reasons why promises are better than callbacks:
- They are built over callbacks and very efficient abstractions.
- They allow cleaner and better functional code.
- They end up with fewer error-prone boilerplate.
- They provide a catching mechanism that is not available in Callbacks.
- You have a superior level of control and trust while delegating tasks through promises rather than callbacks.
There are three HTTP methods in NodeJS. They are:
- http.createServer(): This is used to create a new instance of the http.server class.
- http.request(): This is used for making an HTTP request to the server by creating an instance of the http.ClientRequest class.
- http.get(): It is very much similar to the http.request() method, but it automatically sets the HTTP method to GET and calls the req.end().
A UUID is a Universal Unique Identifier is a method for generating ids that have been standardized by the Open Software Foundation (OSF).
You can generate UUIDs in Node.js through the node-UUID. It is a speedy and straightforward way of generating Version 1 & 4 UUIDs.
Here's how to generate UUIDs
- Install the node-uuid through the npm manager using
npm install uuid. - Use it in your script like this:
const uuidv1 = require('uuid/v1')
const uuidv4 = require('uuid/v4')
var uuid1 = uuidv1()
var uuid5 = uuidv4()
Here is how your output would look. Although, due to the nature of UUIDs, your generated IDs may be completely different.
Output
uuid1 v1 => 6bf958f0-95ed-17e8-sds37-23f5ae311cf6
uuid5 v4 => 356fasda-dad8d-42b7-98b8-a89ab58a645e
The easiest way to debug an application on Node.js is through Node-Inspector. You can use it from any browser supporting WebSockets. It helps multiple ways of debugging like a profiler, livecoding, breakpoints, etc. Here's how to use node-inspector:
- Install it using
npm install -g node-inspector - Now, run
node-debug app.js
Middleware functions are those functions having access to the request object (req), the response object (res), and also the next function in an application's request-response cycle. The following function is basically a function in the Express router, when invoked, executes the middleware which is succeeding in the current middleware.
Middlewares can perform the following tasks:
- Execute any type of code
- Making changes to the request and response objects
- We are ending the request-response cycle.
- Cleaning the next middleware in the stack
| Observables | Promises |
|---|---|
| These are used for streams of events over time. | It is able to handle only one event. |
| It supports operators such as map, filter, reduces, etc., and is cancel-able and retry-able. | It is not easy to handle and returns a single value. |
| It provides chaining and subscriptions for handling complex applications. | It uses only the .then() clause. |
| Here the subscribe method is used for a centralized and predictable error handling. | It pushes the errors to the child's promises. |
Note: This node js interview questions have been created by seasoned Node.js experts. It shall help you to answer some of the most frequently asked questions during a job interview.
Tracing is a mechanism in Node.js to provide a centralized tracing information method, which is generated by V8, Node.js core, and the userspace code. It can be enabled with the --trace-event-categories command-line flag or by using the trace_events module.
CORS is a Node.js package used for providing a Connect/Express middleware.
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "Origin, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept");
next();
});
A callback function is an asynchronous equivalent for a function. It's called at the completion of each and every task. In Node.js, callbacks are generally used, and all the APIs of Node are written in a way to support callback functions.
When a function starts reading a file, it returns the control to the execution environment immediately so that the next request can be executed, and this is a perfect example of a callback function.
Here’s how to write a callback function in Node.js:
var myCallback = function(data) {
console.log('got data: '+data);
};var usingItNow = function(callback) {
callback('get it?');
};
The spawn is a method in NodeJS that spawns an external application through a new process and finally returns a streaming interface for I/O. It is excellent for handling applications that produce a large amount of data or for working with streams of data as it reads in.
Here’s an example how child process have the ability to use the spawn method:
const { spawn } = require('child_process');
const ls = spawn('ls', ['-lh', '/usr']);ls.stdout.on('data', (data) => {
console.log(`stdout: ${data}`);
});ls.stderr.on('data', (data) => {
console.error(`stderr: ${data}`);
});ls.on('close', (code) => {
console.log(`child process exited with code ${code}`);
});
Here are the pros of using promises over callbacks:
- Better defined and organized control flow of asynchronous logic.
- Highly reduced coupling.
- We have integrated error handling.
- Enhanced readability.
Cons of using Promises over callbacks:
- It kills the purpose of asynchronous non-blocking I/O.
- Only one object can be returned.
- We cannot return multiple arguments.
Authorization is handled by calling passport.authorize(). If the authorization is granted, the result by the verify callback shall be assigned to the req.account.
Here's how authorization of a Twitter account is handled in Passport.
app.get('/connect/twitter',
passport.authorize('twitter-authz', { failureRedirect: '/account' })
);app.get('/connect/twitter/callback',
passport.authorize('twitter-authz', { failureRedirect: '/account' }),
function(req, res) {
var user = req.user;
var account = req.account;account.userId = user.id;
account.save(function(err) {
if (err) { return self.error(err); }
self.redirect('/');
});
}
);
Here are some best practices to make your NodeJS application secure:
- Limit the number of concurrent requests through middleware such as cloud firewalls, cloud load balancers, etc.
- Adjust the HTTP response using secure headers for enhanced security and blocking vulnerabilities such as XSS, clickjacking, etc.
- Use a secure hash + salt function such as bcrypt to store passwords, API keys, and secrets instead of Node.js crypto library.
- Limit brute-force authorization attacks by limiting the number of failed login attempts and, in such a case, ban the user's IP address.
- Limit your payload size by using a reverse-proxy or a middleware.
- Avoid pushing secrets on to the npm registry.
- Use cookies securely
- Ensure the security of all your dependencies
Global objects are those who provide variables and functions that are available anywhere within the code. By default, they are those objects which are built into the language or the environment.
All the properties of Global Objects can be accessed directly in node.js using the window.
window.currentUser = {
name: "Best Interview Question"
};
Fork() is used to spawn a new Node.js process. It invokes a specific module with an IPC communication channel, thus enabling the sending of messages between a parent and child.
const { fork } = require('child_process');
const forked = fork('child.js');
forked.on('message', (msg) => {
console.log('Message from child', msg);
});forked.send({ hello: 'world' });
| Child Process | Clusters |
|---|---|
| It is a module of Node.js containing sets of properties and functions helping developers throughout the forking process. | These can be easily spun using Node's child_process module and can communicate with each other using a messaging system. |
| It occurs when you have two or more node instances running with one master process routing. | It spawns a new script or executable on the system. |
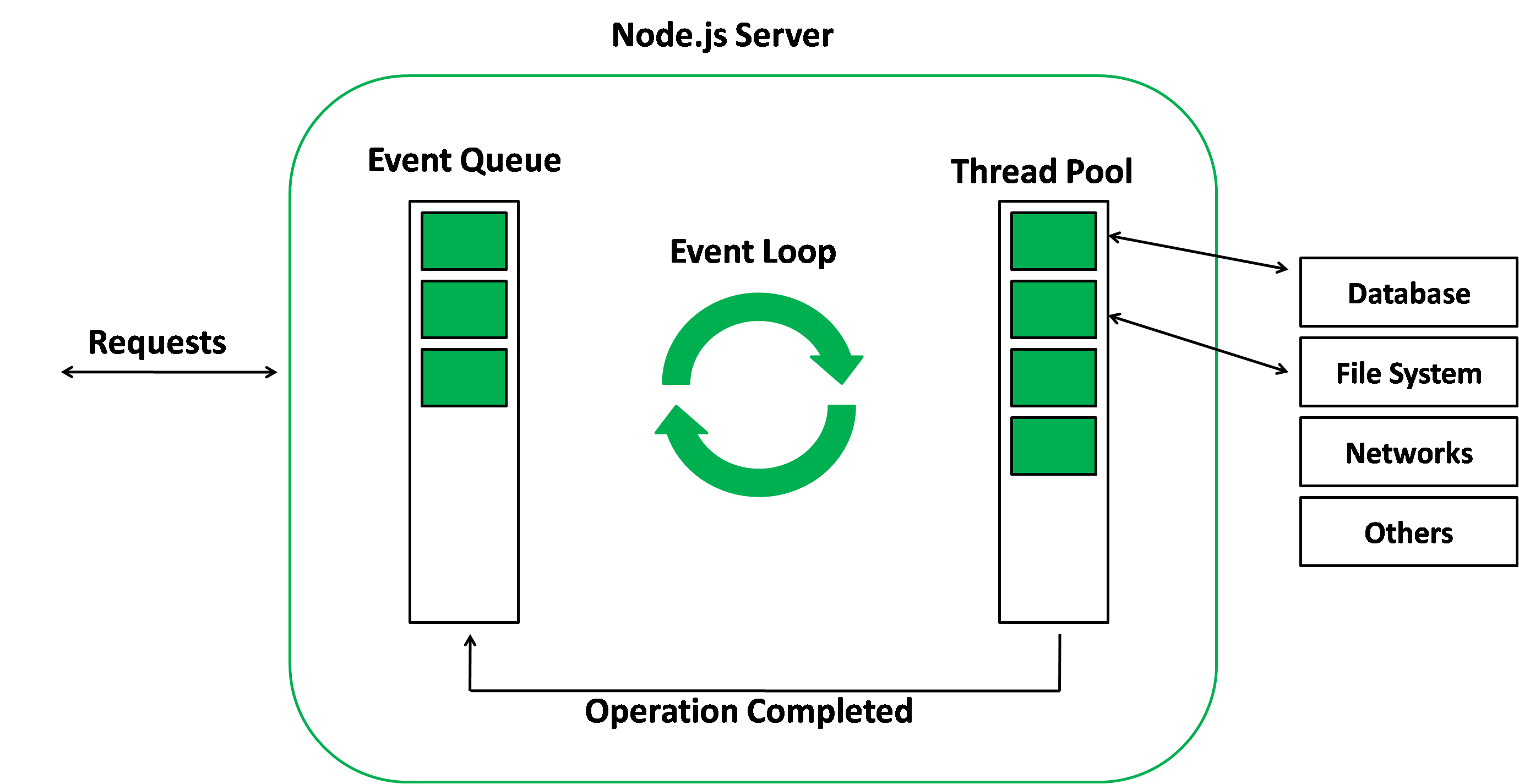
The event loop is the thing that allows Node.js to operate the non-blocking input/output operations. Despite the originality, JavaScript is a single-threaded that is used for offloading the operations to the kernel of the system, when possible.
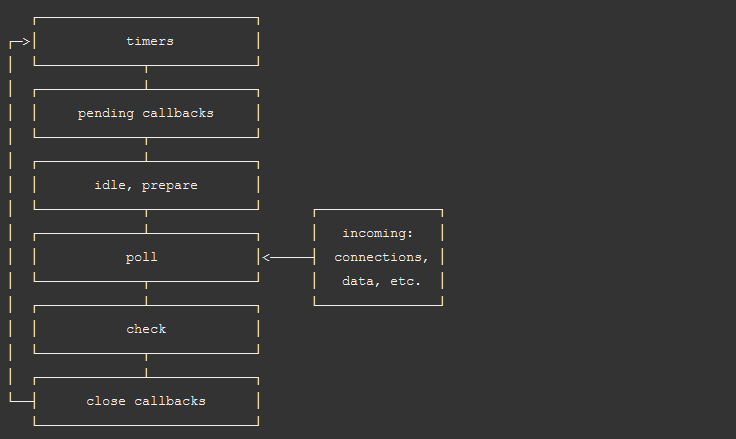
Phases of the Event loop
- Timers
- Pending Callbacks
- Idle, Prepare
- Poll
- Check
- Close Callbacks
console.log("This is first title");
setTimeout(function(){
console.log("This is second title");
}, 1000);
console.log("This is third title");OUTPUT
This is first title
This is third title
This is second title
Multiple reasons are listed below:
- In the comparison of HTTP servers, it provides the non-blocking of the input/output.
- Node reduces the total number of servers that serve an equal amount of requests.
- This uses the single process for managing the multiple requests.
- By using the single-thread process, the computing speed will get increased and it also saves a lot of space.
Async and await are used to make the code easier to write and read. Also, the agenda behind rolling out this feature is to deal with the promises and functions chaining in the Node. Where the functions do not need to be chained just one after another, simply call the await function that returns the promise. On the other hand, the function async should be declared before returning a promise by awaiting a function.